Towards a relevant Data Governance Strategy

What is Data Governance really?
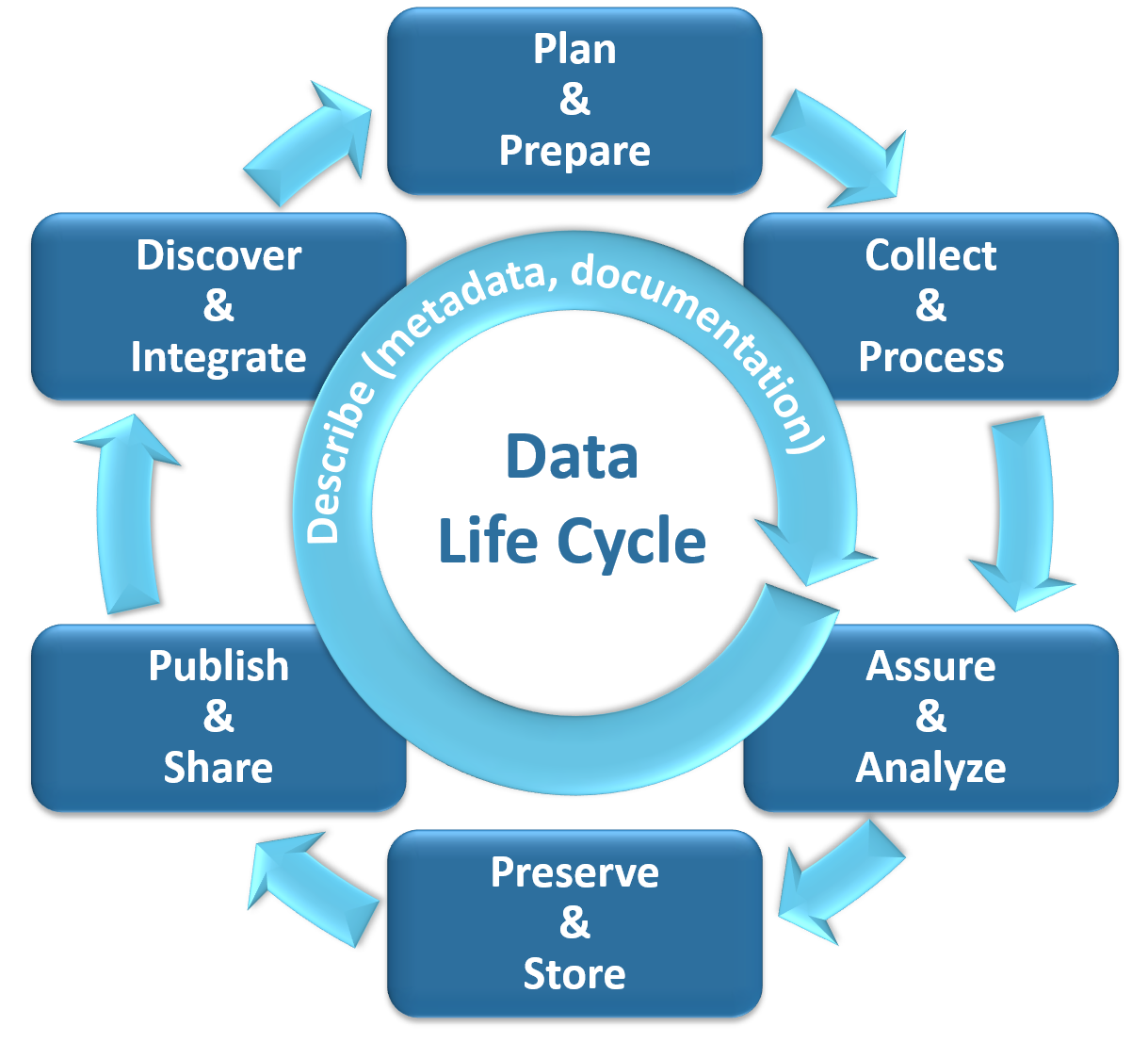
Data governance refers to the exercise of authority and control over the management of data. It aims to increase the value of data and minimize data-related cost and risk (Abraham &al, 2019). Data governance is characterized by frequent jurisdictional overlap and actors in the field clash about their conflicting visions of what data governance should achieve or avoid (kevinejabj, 2022). Organizations need to adopt an appropriate data governance program to strike a balance between value creation and risk and cost (Miura, 2022). Without formal data governance, disconnected and unregulated data requirements often result in duplicative data storage and invalid data ( & Lehman, 2011). Data governance involves the set of principles, values, and standards that guide decision-making among stakeholders who create, manage, and use data. It can contribute to improving public transparency by improving data management and facilitating decision-making regarding data's use and quality (Cerrillo-Martínez & Casadesús-de-Mingo, 2021).
1. Rene, Abraham., Johannes, Schneider., Jan, vom, Brocke. (2019). Data governance: A conceptual framework, structured review, and research agenda. International Journal of Information Management, doi: 10.1016/J.IJINFOMGT.2019.07.008
2. kevinejabj. (2022). Data Governance. doi: 10.1093/oso/9780192870193.001.0001
3. Kazuki, Miura. (2022). Data Governance. Classroom companion: business, doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19554-9_3
4. Debra, Wilbanks., Karen, Lehman. (2011). Data governance for SoS. International Journal of System of Systems Engineering, doi: 10.1504/IJSSE.2012.052698
5. Agustí, Cerrillo-Martínez., Anahí, Casadesús-de-Mingo. (2021). Data governance for public transparency. Profesional De La Informacion, doi: 10.3145/EPI.2021.JUL.02
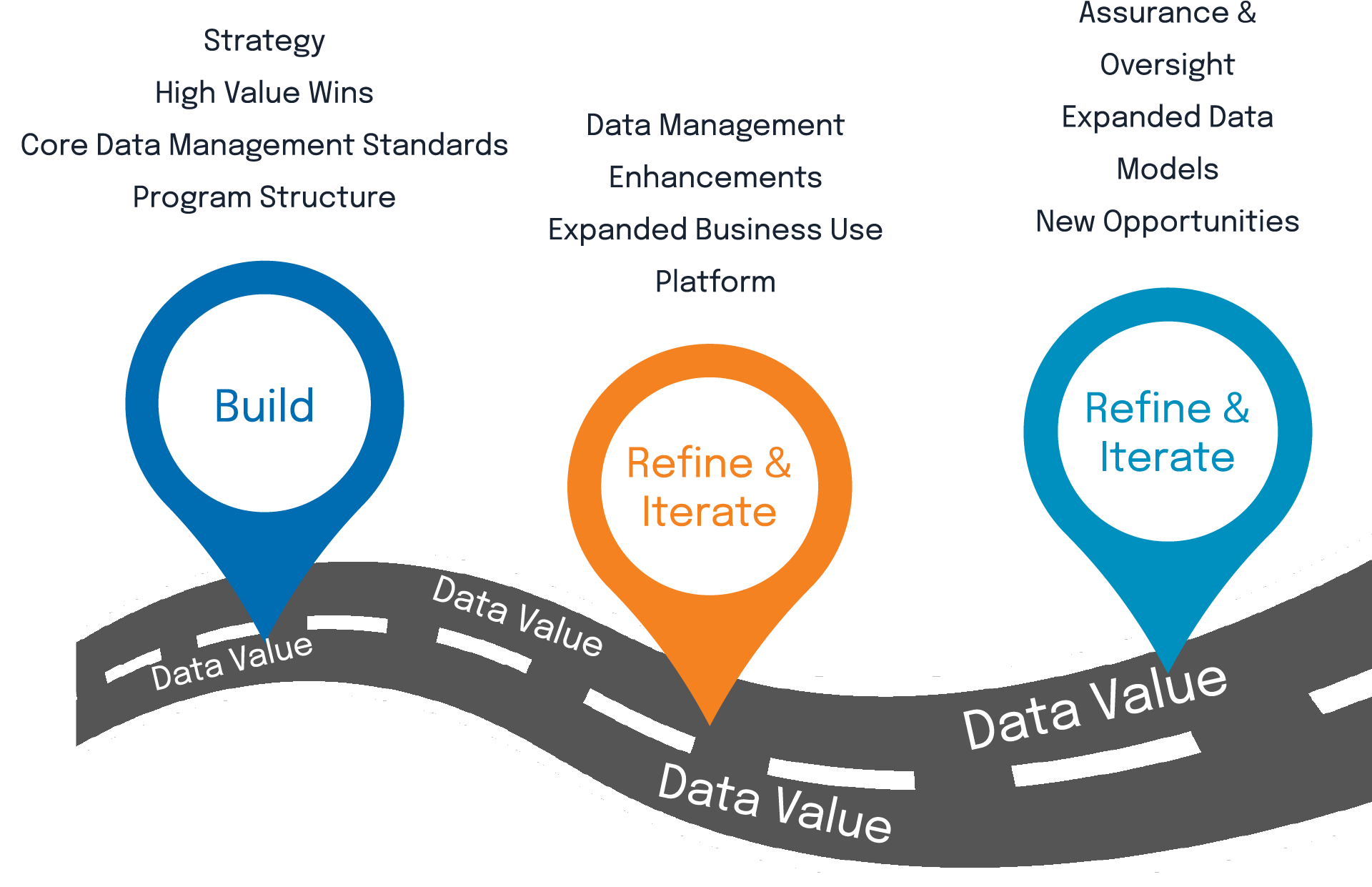
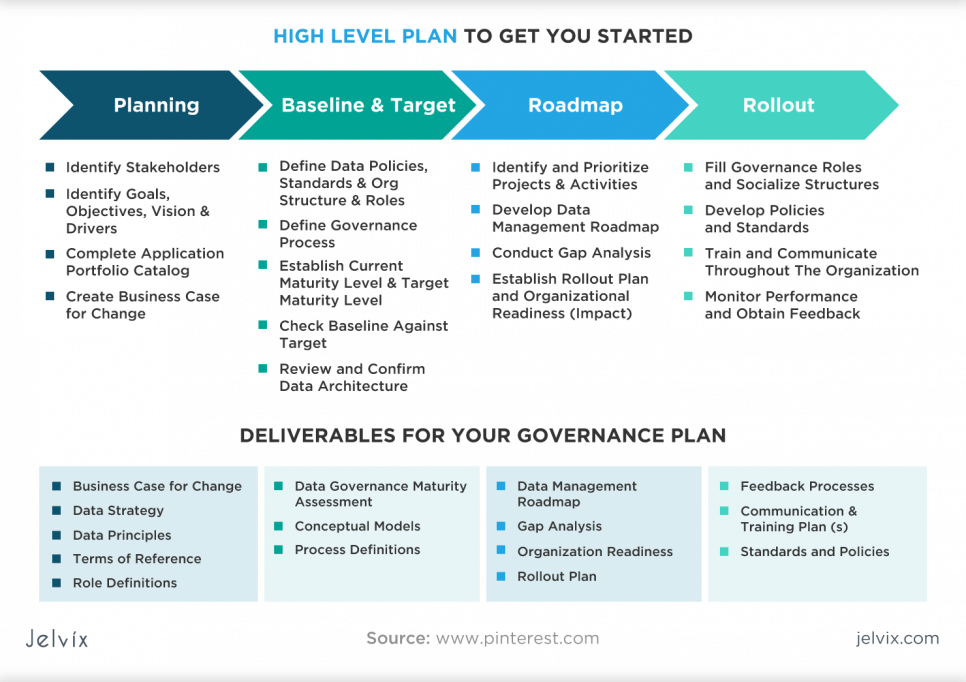
Is there an integrated model for a sustainable data governance process?
Nowadays, Data governance, integration, and management face several challenges. The complexity of data usage in businesses has led to the need for effective data governance solutions (Al-Qahtani & Rahman, 2023). However, the implementation of data governance has been hindered by factors such as IT-driven processes and inadequate support from organizations (Stanescu. & Onufreiciuc, 2020). Global data governance also presents challenges due to the lack of an overarching framework for protecting consumer data and the complexities of Internet-based technologies (Kuzio & al, 2022). Organizations need to adopt appropriate data governance programs to balance value creation, risk and cost (Miura, 2022). Additionally, data governance must address challenges such as data silos, data consistency, privacy, security, and access control (Jaberzadeh & al, 2023). To overcome these challenges, a comprehensive framework integrating data trust, blockchain, and smart contracts can facilitate secure and mutually beneficial data sharing while ensuring incentives, access control, and penalizing dishonest behavior .

1. Al-Qahtani, K. S. et Rahman, M.M.H. (2023). Data Governance and Digital Transformation in Saudi Arabia. Studies in Autonomic, Data-driven and Industrial Computing, doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-7528-8_8
2. Lorena, Elena, Stanescu., Raluca, Onufreiciuc. (2020). Some Reflections on 'Datafication': Data Governance and Legal Challenges. doi: 10.18662/ELJPA/7.1/118
3. Jacqueline, Kuzio., Mohammad, Hadi, Ahmadi., Kyoung-Cheol, Kim., Michael, R., Migaud., Yi-Fan, Wang., Justin, B., Bullock. (2022). Building better global data governance. Data & policy, doi: 10.1017/dap.2022.17
4. Kazuki, Miura. (2022). Data Governance. Classroom companion: business, doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19554-9_3
5. Jaberzadeh, A., Shrestha, K. A., Khan, A. F., Shaikh, A. M., Dave, B., et. al. (2023). Block chain-Based Federated Learning: Incentivizing Data Sharing and Penalizing Dishonest Behavior. J Electrical Electron Eng, 2(4), 353-358.
Data Governance VS Data Science
Data governance and data science are closely related fields that involve the management and analysis of data. Data governance refers to the processes and policies in place to ensure the availability, integrity, and security of data, while data science involves the use of data to gain insights and make predictions. In the context of biodiversity science, researchers and Indigenous Peoples are developing governance principles, such as the FAIR and CARE Principles, to address the colonial history and inequities in biodiversity data management (Sterner & Eliott, 2023). In the analysis of materials structure and activity relationships, data quantity governance is important to address the mismatch between sample size and feature space, and specific ML approaches are used to tackle this issue (Liu & al, 2023). Data integrity and data governance are crucial for ensuring the consistency, trustworthiness, and regulatory compliance of data in enterprise systems (Kumar, 2023). In the MENA region, open data and open science practices are being investigated to identify gaps and opportunities for economic development, using a national data governance approach (Ekundayo & Isaac, 2023). Data governance in the governance of digital data involves resolving overlapping claims and normative differences among different actors, with different visions of what data governance should achieve (kevinejabj, 2022).

Beckett, Sterner., Steve, Elliott. (2023). How data governance principles influence participation in biodiversity science. Science As Culture, doi: 10.1080/09505431.2023.2214155
Yue, Liu., Zhengwei, Yang., Xinxin, Zou., Shuchang, Ma., Dahui, Liu., Maxim, Avdeev., Siqi, Shi. (2023). Data quantity governance for machine learning in materials science. National Science Review, doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwad125
B. Santhosh Kumar (2023). Data Integrity and Data Governance. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.100778
Tosin, Ekundayo., Osama, Isaac. (2023). Open Data: A National Data Governance Strategy for Open Science and Economic Development - A case study of the United Arab Emirates. doi: 10.54878/ejbess.208
kevinejabj. (2022). Data Governance. doi: 10.1093/oso/9780192870193.001.0001